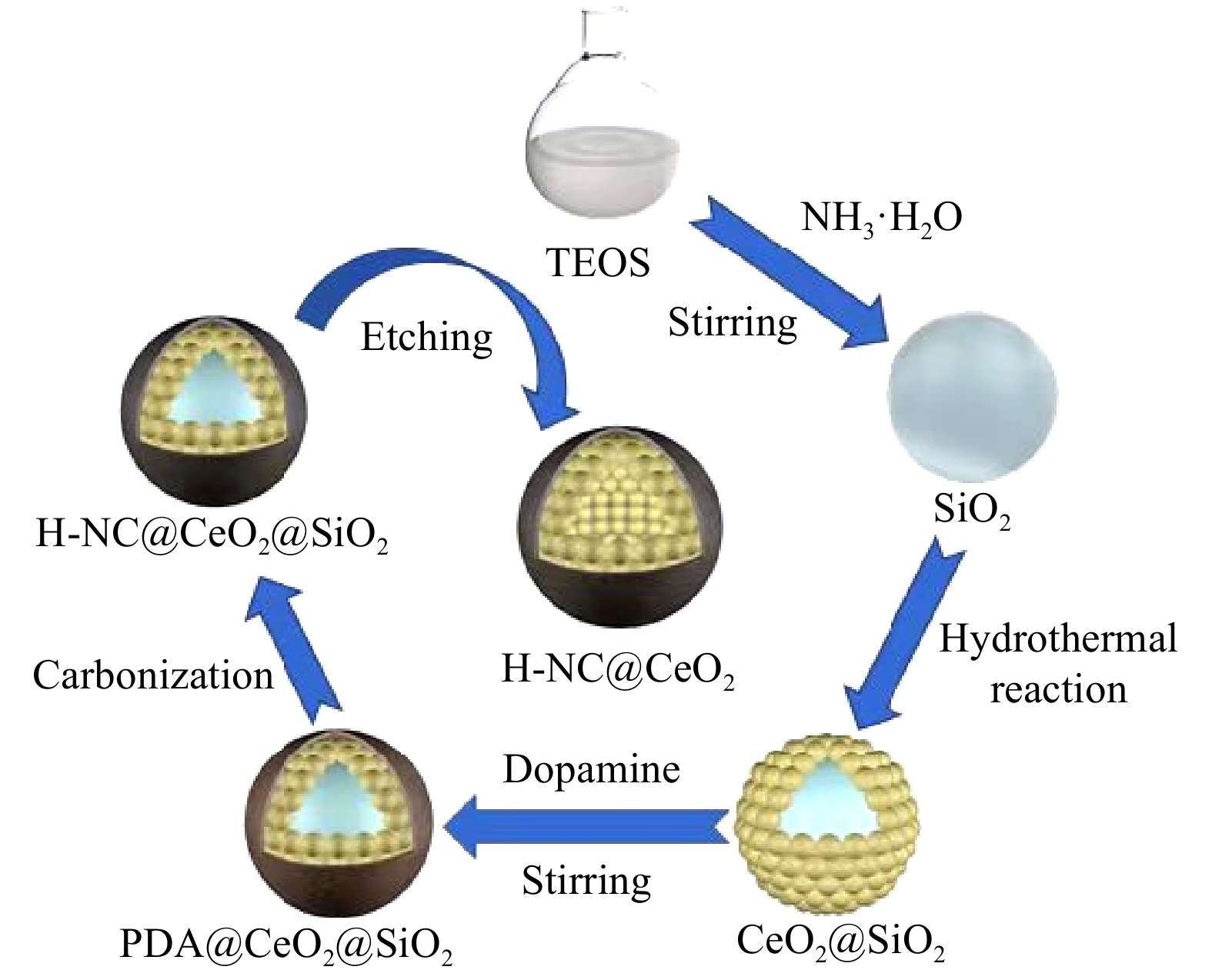
(a) Simulated electric field distribution and (b) volume loss density distribution of the honeycomb structure; (c) simulated electric field vector distribution on the top surface and (d) simulated magnetic field vector distribution within the honeycomb structure (E is electric field strength, H is magnetic field strength).
Figures of the Article
-
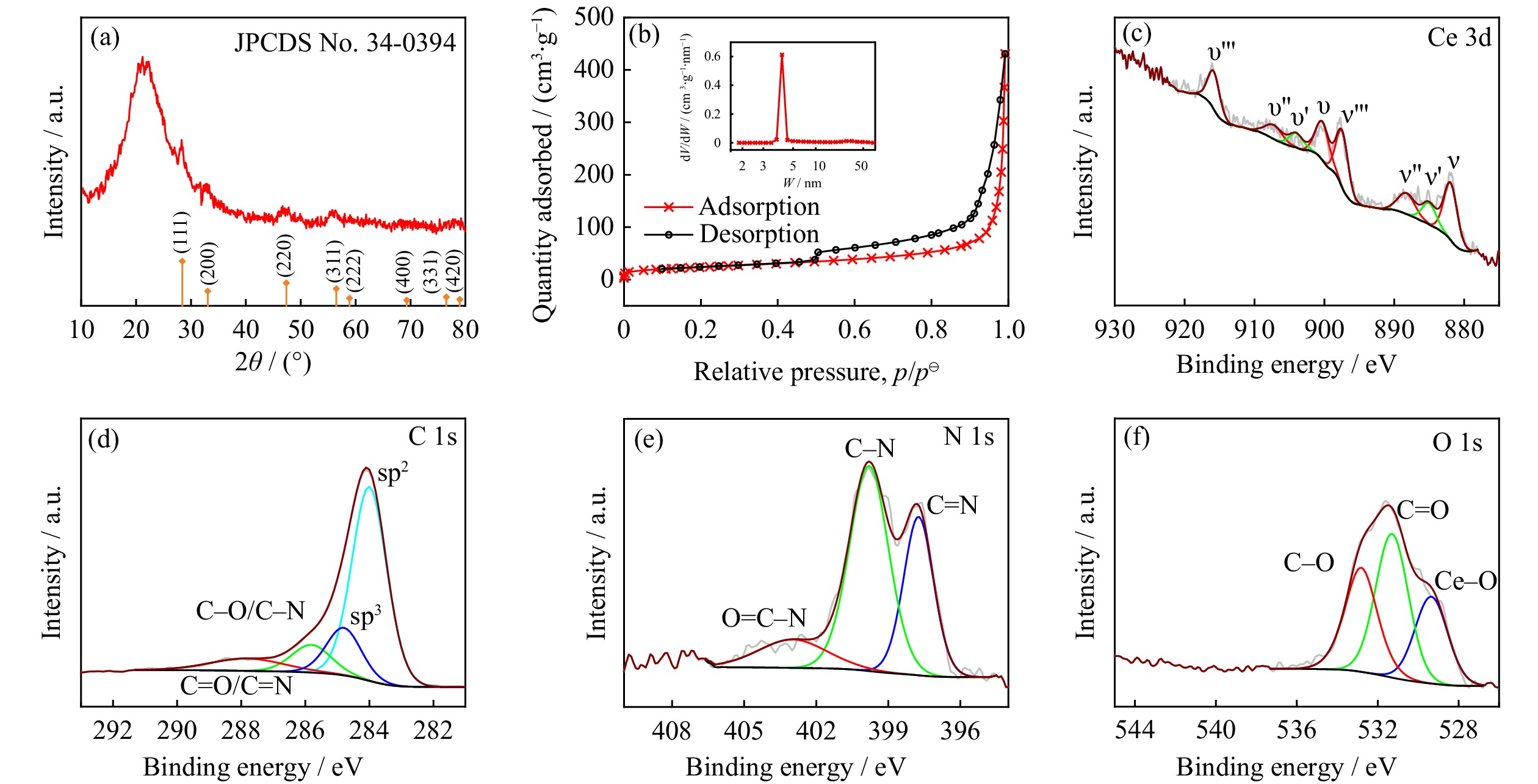
![]() Schematic for the synthesis of H-NC@CeO2 composites (TEOS: tetraethyl orthosilicate, PDA: polydopamine).
Schematic for the synthesis of H-NC@CeO2 composites (TEOS: tetraethyl orthosilicate, PDA: polydopamine).
-
![]() (a) TEM image, (b) SAED image, and (c) high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) image of the H-NC@CeO2 hollow nanospheres; (d) EDS mapping of H-NC@CeO2 for C, N, O and Ce elements.
(a) TEM image, (b) SAED image, and (c) high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) image of the H-NC@CeO2 hollow nanospheres; (d) EDS mapping of H-NC@CeO2 for C, N, O and Ce elements.
-
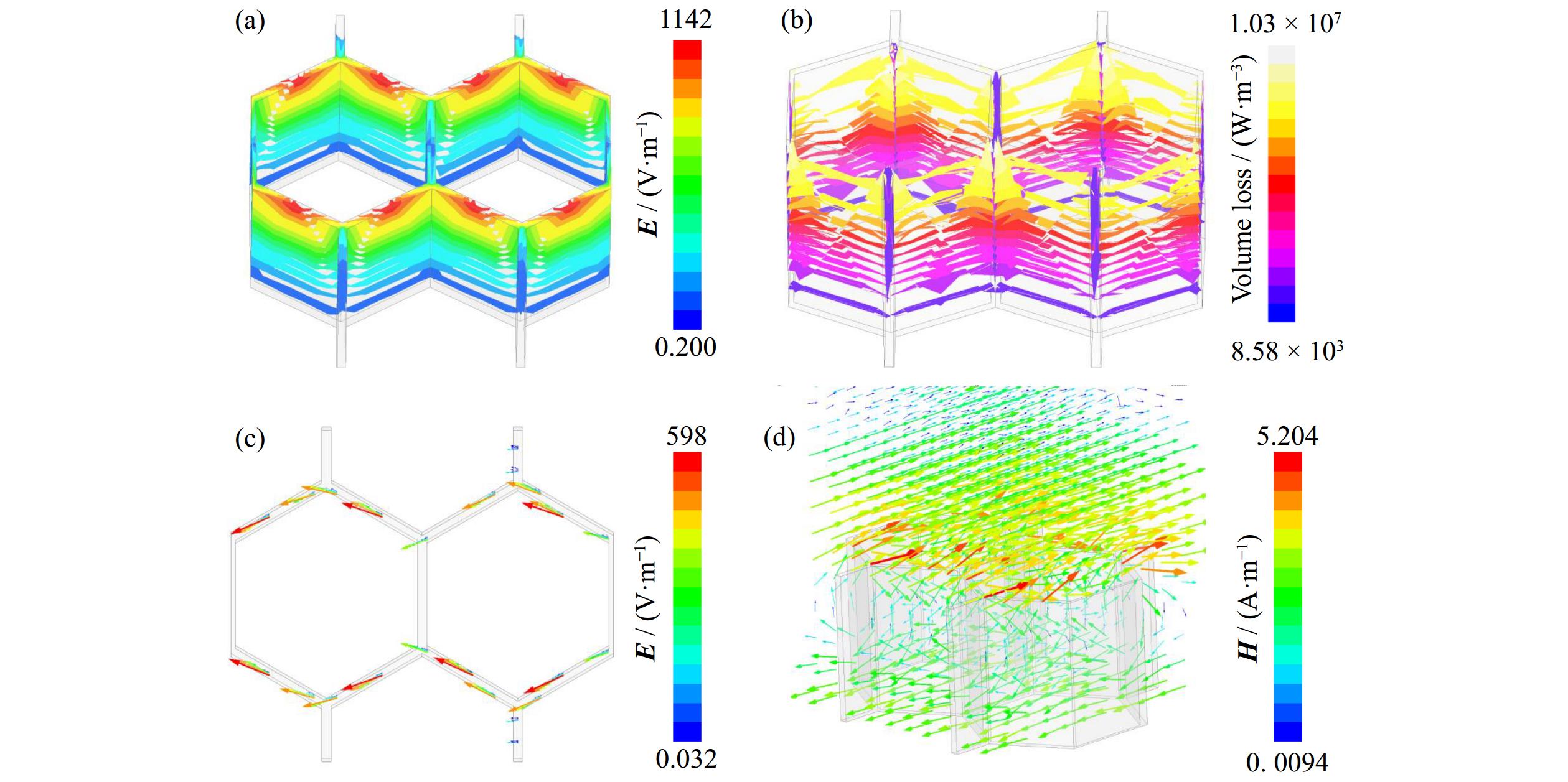
![]() (a) XRD pattern of H-NC@CeO2; (b) nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm and the associated pore size distribution of H-NC@CeO2; and XPS fine spectra of H-NC@CeO2 for (c) Ce 3d, (d) C 1s, (e) N 1s, and (f) O 1s, respectively (p represents the actual pressure of the gas, p⊖ denotes the saturated vapor pressure of the gas at the measurement temperature, V represents pore volume, and W represents pore width).
(a) XRD pattern of H-NC@CeO2; (b) nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm and the associated pore size distribution of H-NC@CeO2; and XPS fine spectra of H-NC@CeO2 for (c) Ce 3d, (d) C 1s, (e) N 1s, and (f) O 1s, respectively (p represents the actual pressure of the gas, p⊖ denotes the saturated vapor pressure of the gas at the measurement temperature, V represents pore volume, and W represents pore width).
-
![]() Value for real permittivity and imaginary permittivity of H-NC@CeO2/PS with (a) 5wt%, (b) 10wt%, (c) 15wt%, (d) 20wt%, (e) 25wt%, and (f) 30wt% filling ratios.
Value for real permittivity and imaginary permittivity of H-NC@CeO2/PS with (a) 5wt%, (b) 10wt%, (c) 15wt%, (d) 20wt%, (e) 25wt%, and (f) 30wt% filling ratios.
-
![]() 3D RL values for H-NC@CeO2/PS with filling ratios of (a) 5wt%, (b) 10wt%, (c) 15wt%, (d) 20wt%, (e) 25wt%, and (f) 30wt% at different thicknesses.
3D RL values for H-NC@CeO2/PS with filling ratios of (a) 5wt%, (b) 10wt%, (c) 15wt%, (d) 20wt%, (e) 25wt%, and (f) 30wt% at different thicknesses.
-
![]() Schematic diagram of microwave absorption mechanisms for H-NC@CeO2 composites under multiscale.
Schematic diagram of microwave absorption mechanisms for H-NC@CeO2 composites under multiscale.
-
![]() Absorption performance metrics for the designed honeycomb include: (a) at r = 10 mm, dwall = 0.5 mm, and h = 10 mm; (b) across dwall values from 0.5 to 2.0 mm; (c) with inner diameters r ranging from 6 to 10 mm; (d) for varying heights h from 5 to 10 mm.
Absorption performance metrics for the designed honeycomb include: (a) at r = 10 mm, dwall = 0.5 mm, and h = 10 mm; (b) across dwall values from 0.5 to 2.0 mm; (c) with inner diameters r ranging from 6 to 10 mm; (d) for varying heights h from 5 to 10 mm.
-
![]() (a) Simulated electric field distribution and (b) volume loss density distribution of the honeycomb structure; (c) simulated electric field vector distribution on the top surface and (d) simulated magnetic field vector distribution within the honeycomb structure (E is electric field strength, H is magnetic field strength).
(a) Simulated electric field distribution and (b) volume loss density distribution of the honeycomb structure; (c) simulated electric field vector distribution on the top surface and (d) simulated magnetic field vector distribution within the honeycomb structure (E is electric field strength, H is magnetic field strength).
Related articles
-
2025, vol.32,no.3,pp.566-577. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-024-3024-3
-
2016, vol.23,no.10,pp.1150-1156. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-016-1334-9
-
2016, vol.23,no.5,pp.534-541. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-016-1264-6
-
2014, vol.21,no.2,pp.150-154. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-014-0878-9
-
2011, vol.18,no.2,pp.165-168. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-011-0417-x
-
2009, vol.16,no.5,pp.554-558. DOI: 10.1016/S1674-4799(09)60095-9
-
2008, vol.15,no.4,pp.451-456. DOI: 10.1016/S1005-8850(08)60085-7
-
2007, vol.14,no.6,pp.538-542. DOI: 10.1016/S1005-8850(07)60124-8
-
2007, vol.14,no.5,pp.460-463. DOI: 10.1016/S1005-8850(07)60090-5
-
2005, vol.12,no.4,pp.329-334.



 Search
Search
 Download:
Download: